Research Article :
As wireless broadband
communication has been experiencing a tremendous growth in past few year, the
demands for various new & advanced multiple access techniques is increasing
consistently. We can experience many new multiple access techniques in 3G &
4G. Here in this article we propose the multiple access technique IDMA which
was developed with the view of achieving something more in terms of speed and
capacity then what we had in 3G. The most important in IDMA is turbo-code which
has increased the efficiency of 4G to a larger extent. By using these turbo
codes with interleave division multiple excess the data rates 4G technology has
been increased significantly. The basic idea behind this article is to lead
down how by using interleaver division multiple accesses we can achieve higher
coding gain, capacity, high speed (both for uploading & downloading) by
using turbo codes along with IDMA. As we go ahead in the current
scenario of wireless digital communication, multiple access technique has been
significant nowadays. Over the years, the need for high bandwidth, high
efficiency, and high data rate has increased to a larger extent. To meet this
ever-growing demand has lead down the foundation of most innovative Multiple
Access Technique viz. IDMA (Interleave Division Multiple Access). The main
reason to switch to IDMA from OFDM is the complexities that were observed in
OFDM. In OFDM, for all the signals to maintain orthogonality amongst themselves
was the major challenge and many times it can be observed that even if a single
signal on the entire bandwidth losses orthogonality then all the signals on
that bandwidth are affected. To overcome all theses IDMA was introduced which
works on a different principle than that of OFDM and gives a much better way of
communication. Before starting with all the
concepts involved in both OFDM (for better understanding) and IDMA it is to
understand the influence of multiple access technologies I communication
system. Whenever a signal is transmitted from mobile to base station or vice versa,
the signal uses a dedicated bandwidth, this bandwidth is been allocated to
multiple users from its respective service providers; the multiple access
techniques allows all the users to communicate with the base station of its
respective service providers or with any other users of any particular service
providers efficiently. This is due to the reason that the spectrum of allocated
bandwidth is high but limited with respect to the load of number of users
occupying it, and owing to this there a very high probability that signal may
get faded, her multiple access techniques helps in sharing the capacity of the
bandwidth over the given region and allows the signal to flow flawlessly.
During this process of signal propagation, multiple access techniques also take
care that the quality of the signal should remain distinct the propagation. When we go across to 4G from 1G,
all the communication system have got its own multiple access techniques,
therefore it can be stated that multiple access techniques are something that
can be taken as the introductory node of all the communication technologies.
The one used in 3G is OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing), this
has given a huge boost not only to 3G but it has led down the foundation of
modern communication with 3G that has excelled to give best date rates within
very few time and with the best speed. IDMA (Interleave Division Multiple
Access) was brought to the world when it was realizing the need to overcome the
complexities in OFDM which are discussed further in the article. IDMA is also
called as the advanced version of CDMA [2], where the problem of MUD which was
the huge set back in CDMA is easily overcome [1]. Let us now see the details of
it in the further sections. The very first thing that needs
to understand is: Interleaver is the heart of IDMA system. IDMA is often called
as the next generation multiple access techniques for CDMA [2] and also for
OFDM. In IDMA different users can use different types of Interleavers mentioned
in the further section and also interleavers are used to differentiate the
signals on entire bandwidth spectrum [3]. Since different users are using
different interleavers it optimizes ISI [2]. Interleaver works in a very
special fashion where the data at the input end of interleaver is in matrix
form, the matrix takes the data row-wise and the output of the matrix is
column-wise [2]. The most important thing in
interleaver is that it is not mandatory for the signals to be orthogonal as it
is in OFDM [2], and this reduces the complexities of IDMA to a greater extent
[4]. This is the main reason why IDMA was brought up than OFDM (as discussed in
the previous section), because in OFDM for all the signals that are propagating
it is very much necessary to be orthogonal and in case any signal losses its
orthogonality then ISI can easily occur. This behavior of signal fading is
overcome by the use of IDMA (interleavers).and this gives the better quality of
signals at the receiving end. This also enables IDMA to give better data rates,
improved bandwidth efficiency where the entire bandwidth can be utilized in an
optimized manner [4]. Design
of IDMA System As discussed in the previous
section, IDMA is the most versatile multiple access techniques at present in
the communication technology. Let us now have a look at its system model to
have a brief idea of about how exactly the signals are being processed in IDMA
to give the optimistic results. In IDMA system, the main
challenge is to avoid ISI in the non-orthogonal signals, since here signal are
not orthogonal as in OFDM [3]. We also have a multiple access technique named
CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) where the symbols are not orthogonal and
here the symbols are transmitted via asynchronous transmission and due to these
problems like ICI and ISI are encountered in CDMA also the problem of MUD takes
place in CDMA due to this type of transmission [3][4]. Therefore to overcome
all these issues in IDMA is used where all the signal are separated using
interleavers and hence, IDMA can be called as a special form of CDMA [4]. Now, let us get into the details
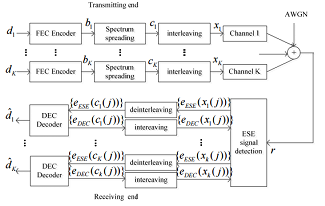
of fig.1 which shows how the symbols are propagating in IDMA. The very first
block is for encoding where the symbols are encoded and processed further to
spread spectrum. Here, at this stage, every signal gets entire bandwidth to use
and here starts the role of multiple access schemes where they need to manage
all the symbols on the allocated bandwidth inefficient manner so as to utilize
the bandwidth up to its best and to yield the best possible results. As per the
discussion in the introduction section, the multiple access technique allows
the signals to propagate through the spectrum, it is very much essential for
multiple access techniques to maintain the capacity of the spectrum intend so
that it can be used at the most. Once the signals channel is
occupied by the signals, all the signals are now interleaved using any of the
interleaving techniques, this forms the unique block of the system where
symbols can be identified based on their respective interleaver, and this helps
to keep the communication easy and faster. Further, the signals sent across to
receiving end via channels wherein between channels and the receiving end the
signals travel across the sky and this is the time when the signal is most
likely is to be affected by interference (MAI). The first block at the receiving end is of ESE
(Elementary Signal Estimator) block, the main function of ESE block is to
detect the interference and it also resolves interference partially. This is
also one of the unique blocks at the receiving end of IDMA system which makes
its special to overcome with interference at the receivers end. Further, the
signals are sent over to deinterleaver where the signal is separated from the
respective interleavers and then passed on for decoding to the block of decoder
post which the signal reaches its destination successfully. The above-mentioned
procedure is repeated for all the signals waiting in the queue for being
transmitted [3].
So far we have seen that,
interleavers form an integral part of IDMA where each signals is interleaved
and transformed. Let us now go in brief about the different types of
interleavers are used to spread the signals across the available spectrum in
various patterns as listed below. This form the easiest way for the
symbols to spread across the spectrum using interleavers. In random
interleavers, the concept of pseudo-random computation is used [5]. All the
symbols that are to be transmitted are scrambled randomly in an arbitrary
fashion [2][4][5][6]. Since the data is scrambled in an arbitrary way this help
to reduce the burst error of the channels at the receiving side [5]. In random
interleavers, data are arranged using an arbitrary series and while decoding at
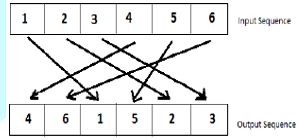
the receiving the same sequence is required to be used. Following is one such
example of data transmission using random interleavers, where at receiver end;
the data can be regenerated using the same series of permuted indices of
generation. Figure 2: Scrambling of data in Random Interleavers. The difficulty of using random
interleaver is that the separation of users will be very difficult in this case
since it will occupy a lot of memory t both transmitter and receiver end [5],
and this will occupy most of its bandwidth making it inefficient for
transmission of multiple symbols which ultimately affect the data rates, also
it will increase the computational complexity at the receiving end as all the
received users will be separated, this may cause the signal to delay and hence
affecting the transmission rate [5].
Master Random Interleavers is
similar to random interleavers in its functioning but it overcomes the
drawbacks encountered in random interleavers. The major setback of random
interleavers is that it is very difficult to separate the users. Here, in this
case, the above-mentioned issue can be avoided. IDMA uses interleavers for
transmission, therefore, it is essential for the BS (Base Station) to store all
the interleavers with the respective patterns used, and therefore interleavers
will definitely consume the memory making the spectrum less efficient to handle
more number of users [6]. Apart from this at an initial stage, it is also
required for BS and MS (Mobile Station) to share the pattern of interleavers
used for communication [6]. To
overpower all this master random interleavers also called as power interleavers
is used, where a master interleaver pattern is assigned [6]. Now let us
understand how this is achieved. The number of interleavers used will surely be
an integer, therefore lets assume thatSince there are interleavers, so the total interleavers
generated can be expressed as. Therefore,
by above principle, every interleaver can be expressed as a power of . The
basic idea here is that, if is an ideal random permutation then all are ,
and these permutations are almost independent of each other [6]. After
the above process is completed, each BS assigns the power index of to each
user, which then generates for user at
MS. The
signals transmitted by this phenomenon of pattern generation increases the
efficiency of the spectrum bandwidth in terms of handling the user signals and
to process it from BS to MS [6]. Tree Based Interleaver (TBI) Main
objective here in tree-based interleaver is to overcome the issue of memory
consumption in random and power interleaver and also to overcome the
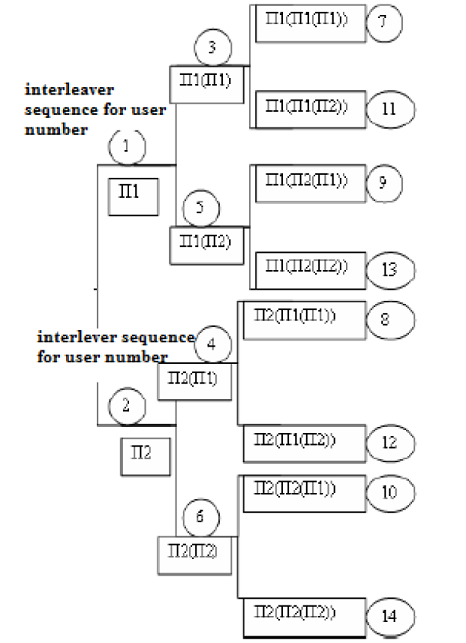
computational complexities encountered in each of them respectively [6]. Figure 3: Masking of interleavers of TBI. The
concept of TBI is quite similar to random interleaver, but here instead of one
interleaver (like in random interleaver) two interleavers are selected at random,
these two interleavers are selected since it is a tree-based concept so it has
got multiple branches as seen in below diagram, so the two interleavers are
selected to separate it out (two interleavers) to 2 different branches observed
in below fig.3 [6]. The two interleavers elected at random are termed as the
master interleavers [6]. The
two interleavers are select in such a way that one is odd and one is even;
where the even number of users goes downside whereas odd goes upside as seen in
fig. 3. The main benefit of using this ideology is that it increases the
utilization of the spectrum up to its optimized level with minimal ISI [6]. Let
us now study how the above-mentioned concept works practically, for this lets
have a look at the fig.3 which symbolizes how TBI is implemented. In the above
diagram, the starting point is mentioned as interleaver sequence for user
number, where each incoming signals is been allotted interleaver. Each incoming
signal is given a unique interleaver in alternate fashion; in the above fig.
the very first signal is given the assigned with interleaver whereas the second
with [6]. Further, the next incoming
signals will be allotted with the interleaver of and the subsequent fourth one with...And so
on this tree progress further as shown in the fig above [6]. In TBI, since the
signals are spread over multiple branches it helps a lot to improve the memory
utilization of the channel as compared with the random interleaver, but somehow
this memory consumption is quite more than master random interleaver [6]. Therefore, TBI
can attain the best utilization of memory across the spectrum bandwidth which
allows transmitting more signals over the channel which in turn increases the
data rate of the system and makes it efficient. Performance Parameter: BER (Bit Error Rate) OF IDMA In digital
communication, various parameters are used to compare the performance of
digital system one over the other, so as to get the better understanding of the
systems that are being compared. The definition of
BER can be stated as “the percentage of bits which are corrupt within the total
available bits; it is usually expressed in the negative power of 10 [7].” BER
indicates that what is the total number of bits that are affected by the total
number of bits that were transmitted [7]. To measure BER, BERT (Bit Error Rate
Testers) is used [7]. BER can be expressed mathematically as [4]: The analysis of
BER has an effect on 3 parameters viz. Bandwidth, Interference and Transmission
Power [7]. Results and Analysis Results and
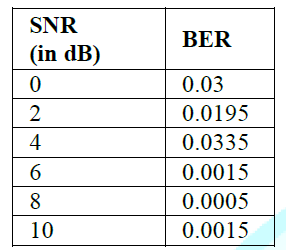
analysis (Chirag Shah et al., 2016) is basically aimed to provide the analysis
of IDMA wrt to BER, which indicates that as the BER value obtained in IDMA is
highly stabilized when the SNR (Signal to Nose Ratio). Where SNR is taken in DB
(decibels). Figure 4: BER response of IDMA System. Table 1: SNR v/s BER values of IDMA (in presence of noise). Conclusion & Future Scope The above study
on IDMA has helped to understand the concept of IDMA clearly; where the focus
was on the key technology in IDMA i.e. interleavers. The main idea of
this article was to have a brief understanding of how the signals are
transmitted through wireless media from transmitter to receiver and how the
signals attains the optimized BER with least possible signal fading. After
going through all the aspects mentioned above it can be concluded that the use
of separate interleavers for each and every signals helps to attain the best
possible results in terms of high data rates, maximum efficiency and the most
important is that it can support a huge number of users to communicate within the
allocated bandwidth spectrum. In regards with
all the above advantages IDMA have got, it will be very interesting to see the
role of IDMA in 5G (where the proposed multiple access technique is BDMA an
advanced version of IDMA) as it has already left an outstanding impact in 4G.
1.
Li
Ping, Lihai Liu, Wu KY, Leung WK. Department of Electronic Engineering, City
University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Interleave-Division Multiple-Access (IDMA)
Communications. 2.
Ekra
Khan, Danish Khan. Evolution OF IDMA (2014) International Journal of Engineering
Science Invention Research & Development 1: 1. 3.
Pragati
NC, Jadhav HM. Implementation of IDMA system for estimation of multiple access
interference (2015) Fourth Post Graduate Conference. 4.
Chirag
R Shah. Performance and Comparative Analysis of OFDM, OFDM–CDMA & OFDM–IDMA
Systems (2016) International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology
(IJERT) 5: 4. 5.
Deepti
sahu, Avinash Shukla, Dayanand Yadav. Generation of Interleaver for IDMA (2014)
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention Research &
Development 1: 2. 6.
Kuldeep
choudhary, P S Sharma. Interleavers for IDMA Technology: A Comparison Survey
(2012) International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and Communication
Engineering 1: 2. 7.
Chirag
R Shah. Analytical and Comparative Analysis of Ofdm, Cdma & Idma Systems
(2016) International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology 42: 5.
A Study on Interleave Division Multiple Access
Abstract
Full-Text
Introduction
IDMA
Principle
Types
of Interleavers
Random
Interleavers
Master
Random Interleavers

References