Research Article :
Suicide has its own trends and path. An
emotional set back may leads to suicide is seemed to happen instantly but it is
not true, it takes times to complete .All most all of us have to experience
death wishes but never reach to that point when said completed. Very few will
reach to that point where assessed. This study has aim to decide the path by
which completion occurs. Study has used the various discrete data of various
studies freely available on internet. They were analyzed and arranged logically
in sequence to set the path and trends. Lot of the people have suicidal ideation but few succeed.
This behavior does not direct to its final destination. It has to proceed in
succession. The aim of this study is to establish the successive stage and
patternize the suicide in different form, require further statistical approval.
The postulated model has four major components that pass through them as a)
ideation b) threat c) attempt d) completion. Ideation may be situational or
persistent .Threat can be seen without self-harm or with self-harm if it occurs
with self-harm can be evident with self-mutilation or deliberate self-harm or
self-throttling. In case if attempts are taken can be identified as true or
threat. If truly taken with ideation which may be situation or momentarily with
or without idea or accidental to proceed further to complete or incomplete.
Completion of suicide may be associated with mental illness a) with
psychotic symptoms
b) without psychotic symptom c) under distress d) under substance influence e)
adjustment problem and associated family conflict 2) without mental illness a)
under serial forced circumstance b) accidental. These are the components that
are identified in clinical practice. The only survivors are negotiable and
those who are psychiatrically ill are assessed with precaution but those who
are free from mental illness remained untouched, need further approval for wide
acceptance. Study of prevalence of suicide ideation across nine diverse
nation has slight variation in life time prevalence rate of suicide rate pr 100
is ranged from 2.09 to 18.51 and attempt ranged from 0.72 to 5.93. Suicide
ideation among female has marginally higher than male but attempt is two to
three folds higher than male each year 300000 death occurred every year and one
million die due to suicide [1-3]. Trend of suicide ideation plan gesture or
attempts are studied from between 1990-1992 and 2001-2003 has no significant changes found in this
study suicidal ideation (2.8% vs 3.3%;
P=.43), plans (0.7% vs 1.0%; P=.15), gestures (0.3% vs 0.2%; P=.24), or
attempts (0.4%-0.6%; P=.45), whereas conditional prevalence of plans among
ideators increased significantly (from 19.6% to 28.6%; P=.04), and conditional
prevalence of gestures among planners decreased significantly (from 21.4% to
6.4%; P=.003). Treatment increased dramatically among ideators who made a
gesture (40.3% vs 92.8%) and among ideators who made an attempt (49.6% vs
79.0%). Conclusions despite a dramatic increase in treatment, no significant
decrease occurred in suicidal thoughts, plans, gestures, or attempts in the
United States during the 1990s. Continued efforts are needed to increase
outreach to untreated individuals with suicidal ideation
before the occurrence of attempts and to improve treatment effectiveness for
such cases. Suicide is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. As a
result, the World Health Organization and the US surgeon general have
highlighted the need [2]. The assumption that information on suicide-related behaviors,
including thoughts, plans, gestures, and nonfatal attempts, is important for
understanding completed suicides can be called into question because only a
small fraction of suicide attempters eventually complete suicide. It is known
stronger predictor of suicide at 5.4%, completed suicide prevalence in this
community cohort of suicide attempters was almost 59% higher than previously
reported [4-5]. An innovative aspect of this study explains the discrepancy: by
including index attempt deaths-approximately 60% of total suicides- suicide
prevalence more than doubled [6-11]. Several study has been conducted to
estimate prevalence of suicide ideation planning and attempt for life time 12
months and 6 months of time has great focus on decreasing trends of these
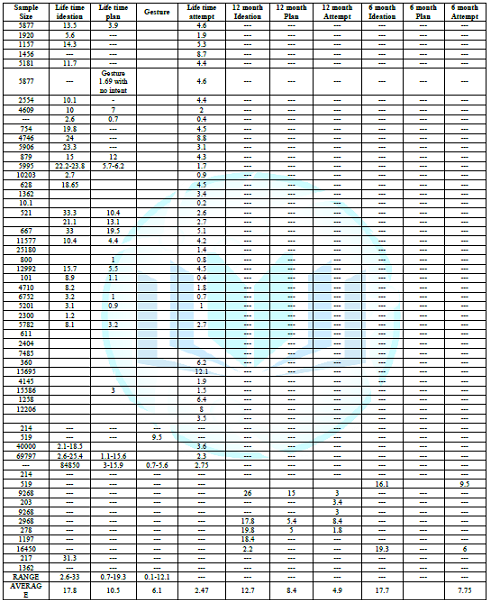
events from 6 months to 12 months and life time .The range and average of
suicide ideation plan and attempt shown in table They showed decreasing trend
but does not fix pattern [12-73]. Table 1: Showed
life time 12 months and 6 months ideation, plan, and attempt [12-73]. Table 2: Showed
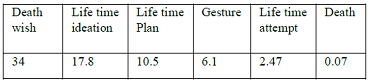
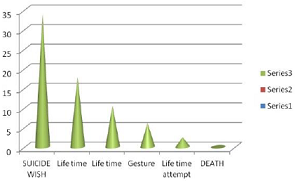
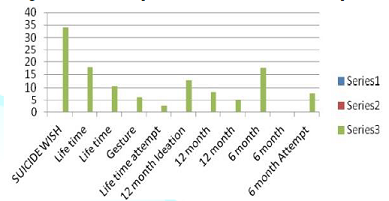
the value of different phenomenon and its graph of their trend. Figure 1: Showed
the prevalence of different suicide phenomena in succession. Figure 2: Showed
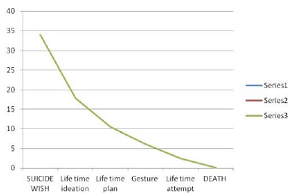
the pattern of suicide forms and their stipness. Table 3: Life
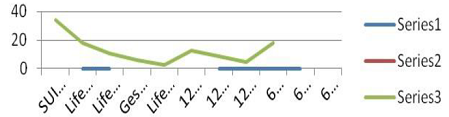
event of suicide overall trends. Figure 4: Showed
trends of all phenomena in the span. To find out path and progression of suicide. Method Observation 1. Prevalence
rate/100 Suicidal ideation 2.09-18.51 Suicidal attempt 0.2-5.93 2. Suicide
ideation; 2.8-3.3 suicide planner; 0.7-1.0; gesture; 0.3-0.2 suicidal attempt;
0.4-0.6 3. 247
relatives suicide completer matched with 171 relatives of matched group of
community comparison AXIS 1 disorder 80% alcohol abuse=44% Depressive disorder
40%, 56%, 24% drug abuse and dependence
AXIS II 56% ,Cluster B-52%, Cluster A-4% , 4% AXIS II in comparison group Linkage study relative of suicide completers
has outnumber of prevalence of aggression depression childhood abuse and
ideation than relatives of non-suicide 4. Suicidal
attempt 148.8 per 100000 person per year and suicide ideation-449.9 per 100000
person years 5. Suicidal
ideation 5.6%, suicidal planner 2.7%, 0.7% suicide attempt 6. N=4866
, suicide ideation 2.4% female, 2.3% male, Para suicide 0.9% in women and 1.1% in male 7. N=700
death wishes 34%, suicidal ideation 12.5%, attempt 2.6% 8. 11583
of DSH, repeated DSH 39%, RR 2.24% of suicide 9. 11583
DSH- Suicide in 5 yrs n=300, RR in 1st yrs e first year of follow-up was 0.7% (95%
CI 0.6-0.9%), which was 66 (95% CI 52-82) times the annual risk of suicide in
the general population. The risk after 5 years was 1.7%, at10 years 2.4% and at
15 years 3.0%. 10. DSH
16 % non-fatal, 2% fatal after 9 yrs 7% suicide. 11. N=11572
ratio between completed suicide and attempted suicide 1: 23 The available data obtained from internet survey arranged in
sequence and its proportion emphasized that death wishes are highest in ranking
followed by attempt and suicide completion [7]. The ration of suicide attempt
and suicide is 1:23 but there is always a gap exist to full fill in between the
suicide ideation and completion [11]. The analysis and visual impact of data
presume that celebrate self-harm fatal and non-fatal repeaters will have to
full fill the gap [8,9,10]. The other factors associated to death completion in
linkage study suggest aggression and impulsivity is force to complete suicide
[3]. Psychiatric co morbid or psychiatric condition
such as mood disorder,
substance use traumatic experiences have role in transmission of ideation or
death wishes to suicide. Considering the average of life time prevalence, 12 month
and 06 month prevalence of suicide as 17.8, 12.7 and 17.7% [3,12-73]. The most
of suicide prevalence exist infinitival 06 month and remained high throughout
the life span and most of the attempt were taken in initial first six months as
mentioned in table above the plan were persistently high throughout the life
span. In all these succession death wishes are 34% statistically it stand far
before the prevalence of life time ideation [7]. DSH 16% non-fatal, 2% fatal
after 9 yrs 7% suicide Deliberate self-harm stands somewhere in between
ideation planning as and attempts [9,11]. The ratio of attempted suicide and completed suicide is
1:23 then it completion in attempted
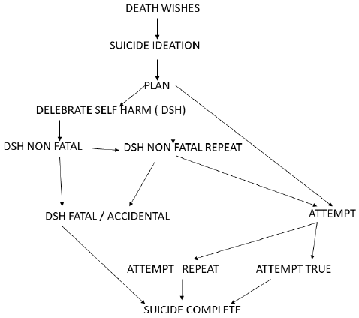
suicide of 2.43% is 0.07%. (y=1*2.43/23). Flow charts -
Represents the successive path to complete suicide. Everyone in their life at least has to wish die but very few
complete it. It progress in certain path as wish further strengthen by idea
following deliberate self-harm may repeat or accidentally completed if not
further proceeds to take attempt. It may be completed or rest as further risk of suicide.
Furthermore the life time plan and plan wit in the 12 months has to prolong
further in their form. The earlier intervention in 06 months duration may
decrease the incidence of suicide and also transition to continue as 12 month
of life time prevalence, plan, and attempt towards completion, may be a
possible explanation. 1. Wiessman
MM, Band RC, Canino GJ, Greenwald S, Hwu HG, et al. Prevalence of suicide
ideation and suicide attempts in nine countries (1999) Psychol med 29: 9-17. 2. Kessler
RC, Patricia B, Berglund P, Borges G, Nock M, et al. Trend in suicide ideation
Plans Gesture and Attempt in United States (2005) JAMA 293: 2487-2495. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.293.20.2487
3. Kuo WH
and Gallo JJ. Completed suicide after a suicide attempt (2005) Am J Psyi 162:
633. 4. Dim K C,
Seguin M, Therrien N, Riopel G, Chawky N, et al. Familial Aggression of
suicidal behaviour: A Family study of male suicide completers from general
population (2005) Am J Psyi 162: 1017-1019. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.162.5.1017
5. Suiminen
K, Isometsa L, Suokas J, Hauka J, Ackte k, et al. Completed suicide after a
suicide attempt: a 37-year follow-up study (2004) Am J psyi 161: 562-563. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.161.3.562
6. Bostwick
JM, Pabbati C, Geske JR and McKean AJ. Suicide attempt is a risk factor for
completed suicide: Even more lethal than we knew (2016) Am J psyi 173: 1094
-1100. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2016.15070854
7. Kuo WH,
Gallo JJ and Tien AY. Incidence of suicide ideation and attempts in adult 13
years follow up of a community in Baltimore Maryland (2001) Psychol Med 31:
1181-1191. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291701004482
8. Crosby
EA, Mark P, Cheltenham BS and Sacks JJ. Suicide and life threating behaviour
(1999) SJR 29: 131-140. 9. Hintkka
J, Viinamaki H, Tanskanen A, Kontula O and Koskela K. Suicidal Ideation and
parasuicide in the finnish general population (1998) Acta Psyi 98: 23-27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.1998.tb10037.x
10. Renberg
ES. Self-reported life-weariness, death wishes, suicidal ideation suicidal
planes and suicidal attempt in general population survey in the north of Sweden
1986 and 1996 (2001) Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 36: 429-436. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.185.1.70
11. Zahl DL and
Hawton K. Repetition of deliberate self-harm and subsequent suicide risk:
long-term follow-up study of 11,583 patients (2004) Br J Psychiatry 185: 70-75.
https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.185.1.70
12. Hawton K,
Zahl D and Weatherall R. Suicide following deliberate self-harm: long-term
follow-up of patients who presented to a general hospital (2003) Br J
Psychiatry 182: 537-542. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.182.6.537
13. Owens D,
Horrocks J and House A. Fatal and non-fatal repetition of self-harm Systematic
review (2002) Br J Psychiatry 181: 193-199. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.181.3.193
14. De Leo D,
Cerin E, Spathonis K and Burgis S. Life time risk suicide ideation and attempt
in an Australian community, Prevalence, suicidal process and help seeking
behavior (2005) J Affect Disord 86: 215-224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2005.02.001
15. Moscicki
EK. The Harvard Medical School guide to suicide assessment and intervention
(Jacobs GD) (Ed) (1999) Epidemiol suicide, Jossey-Bass Publishers, USA, 40-51. 16. Kessler
RC, Borges G and Walters EE. Prevalence of and risk factors for lifetime
suicide attempts in the National Comorbidity Survey (1999) Arch Gen Psyi 56:
617-626. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.56.7.617
17. Dube SR,
Anda RF, Felitti VJ, Chapman DP, Williamson DF, et al. Childhood abuse,
household dysfunction, and the risk of attempted suicide throughout the life
span: findings from the Adverse Childhood Experiences Study (2001) JAMA 286:
3089-3096. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.286.24.3089
18. Ialongo N,
McCreary BK, Pearson JL, Koenig AL, Wagner BM, et al. Suicidal behavior among
urban, African American young adults (2002) Suicide Life Threat Behav 32:
256-271. 19. Garroutte
EM, Goldberg J, Beals J, Herrell R, Manson SM, et al. Spirituality and
attempted suicide among American Indians (2003) Soc Sci Med 56: 1571-1579. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-9536(02)00157-0
20. Joe S,
Baser RE, Breeden G, Neighbors HW and Jackson JS. Prevalence of and risk
factors for lifetime suicide attempts among blacks in the United States (2006)
JAMA 296: 2112-2123. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.296.17.2112
21. Nock MK
and Kessler RC. Prevalence of and risk factors for suicide attempts versus
suicide gestures: analysis of the National Comorbidity Survey (2006) J Abnorm
Psychol 115: 616-623. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.115.3.616
22. Fortuna
LR, Perez DJ, Canino G, Sribney W and Alegria M. Prevalence and correlates of
lifetime suicidal ideation and suicide attempts among Latino subgroups in the
United States (2007) J Clin Psychiatry 68: 572-581. 23. Brenner
ND, Hassan SS and Barrios LC. Suicidal ideation among college students in the
United States (1999) J Consult Clin Psychol 67: 1004-1008. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.67.6.1004
24. Kessler
RC, Berglund P, Borges G, Nock M and Wanget SP. Trends in suicide ideation,
plans, gestures, and attempts in the United States, 1990-1992 to 2001-2003
(2005) JAMA 293: 2487-2495. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.293.20.2487
25. Bertolote
JM, Fleischmann A, De Leo D, Bolhari J,
Botega N, et al. Suicide attempts, plans, and ideation in culturally diverse
sites: the WHO SUPRE-MISS community survey (2005) Psychol Med 35: 1457-1465. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291705005404
26. Alaimo K,
Olson CM and Frongillo EA. Family food insufficiency, but not low family
income, is positively associated with dysthymia and suicide symptoms in
adolescents (2002) J Nutr 132: 719-725. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/132.4.719
27. Eisenberg
ME, Neumark-Sztainer D and Story M. Associations of weight-based teasing and
emotional well-being among adolescents (2003) Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 157:
733-738. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.157.8.733
28. Waldrop
AE, Hanson RF, Resnick HS, Kilpatrick GD, Naugleet EA, et al. Risk factors for
suicidal behavior among a national sample of adolescents: implications for
prevention (2007) J Trauma Stress 20: 869-879. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.20291 29. ODonnell
L, ODonnell C, Wardlaw DM and Ann Stueve. Risk and resiliency factors
influencing suicidality among urban African American and Latino youth (2004) Am
J Com Psychol 33: 37-49. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AJCP.0000014317.20704.0b
30. Centers
for Disease Control and Prevention. National Youth Risk Behavior Survey:
1991-2005: trends in the prevalence of suicide ideation and attempts (2007)
Atlanta, GA. 31. King RA,
Schwab-Stone M, Flisher AJ, Greenwald S, Kramer AR, et al. Psychosocial and
risk behavior correlates of youth suicide attempts and suicidal ideation (2001)
J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psyi 40: 837-846. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-200107000-00019
32. Statham
DJ, Heath AC, Madden PA, Bucholz KK, Bierut L, et al. Suicidal behaviour: an
epidemiological and genetic study (1998) Psychol Med 28: 839-855. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291798006916 33. Kebede D
and Alem A. Suicide attempts and ideation among adults in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
(1999) Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 397: 35-39. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.1999.tb10692.x
34. Akyuz G,
Sar V, Kugu N, Kugua N and Doğan O. Reported childhood trauma, attempted
suicide and self-mutilative behavior among women in the general population
(2005) Eur Psychiatry 20: 268-273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2005.01.002
35. Kjoller M
and Helweg-Larsen M. Suicidal ideation and suicide attempts among adult Danes
(2000) Scand J Public Health 28: 54-61. https://doi.org/10.1080/713797371 36. Ramberg IL
and Wasserman D. Prevalence of reported suicidal behaviour in the general
population and mental health-care staff (2000) Psychol Med 30: 1189-1196. https://doi.org/10.1017/s003329179900238x
37. Rancans E,
Lapins J, Salander Renberg E, et al. Self-reported suicidal and help seeking
behaviours in the general population in Latvia (2003) Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr
Epidemiol 38: 18-26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-003-0602-y
38. Crawford
MJ, Nur U, McKenzie K and Tyrer P. Suicidal ideation and suicide attempts among
ethnic minority groups in England: results of a national household survey
(2005) Psychol Med 35: 1369-1377. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291705005556
39. Mohammadi
MR, Ghanizadeh A, Rahgozart M, Noorbala AA, Malekafzali H, et al. Suicide
attempt and psychiatric disorders in Iran (2005) Suicide Life Threat Behav 35:
309-316. 40. Agoub M,
Moussaoui D and Kadri N. Assessment of suicidality in a Moroccan metropolitan
area (2006) J Affect Disord 90: 223-226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2005.09.014
41. Liu KY,
Chen EY, Chan CL and Lee ST. Socio-economic and psychological correlates of
suicidality among Hong Kong working-age adults: results from a population-based
survey (2006) Psychol Med 36: 1759-1767. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291706009032
42. Ovuga E,
Boardman J and Wasserman D. Undergraduate student mental health at Makerere
University, Uganda (2006) World Psyi 5: 51-52. 43. Bernal M,
Haro JM, Bernert S, Brugha T, de Graaf R, et al. Risk factors for suicidality
in Europe: results from the ESEMED study (2007) J Affect Disord 101: 27-34. 44. Bromet EJ,
Havenaar JM, Tintle N, Kostyuchenko S, Kotov R, et al. Suicide ideation, plans
and attempts in Ukraine: findings from the Ukraine World Mental Health Survey
(2007) Psychol Med 37: 807-819. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291707009981
45. Gureje O,
Kola L, Uwakwe R, Udofia O, Wakil A, et al. The profile and risks of suicidal
behaviours in the Nigerian Survey of Mental Health and Well-Being (2007)
Psychol Med 37: 821-830. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291707000311
46. Lee S,
Fung SC, Tsang A, Liu RZ, Huang QY, et al. Lifetime prevalence of suicide
ideation, plan, and attempt in metropolitan China (2007) Acta Psychiatr Scand
116: 429-437. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.2007.01064.x
47. Nojomi M,
Malakouti SK, Bolhari J and Poshtmashhadi M. A predictor model for suicide
attempt: evidence from a population-based study (2007) Arch Iran Med 10:
452-458. 48. Borges G,
Nock MK, Medina-Mora ME, Benjet C, Lara C, et al. The epidemiology of
suicide-related outcomes in Mexico (2008) Suicide Life Threat Behav 37:
627-640. https://doi.org/10.1521/suli.2007.37.6.627
49. Scocco P
and De Leo D. One-year prevalence of death thoughts, suicide ideation and
behaviours in an elderly population (2002) Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 17:
842-846. https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.691
50. Gunnell D,
Harbord R, Singleton N, Jenkins R and Lewis G. Factors influencing the
development and amelioration of suicidal thoughts in the general population.
Cohort study (2004) Br J Psychiatry 185: 385-393. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.185.5.385
51. Tran Thi
Thanh H, Tran TN, Jiang GX, Leenaars A and Wasserman D. Life time suicidal
thoughts in an urban community in Hanoi, Vietnam (2006) BMC Public Health 6:
76. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-6-76
52. De Leo D,
Padoani W, Scocco P, Lie D, Bille‐Braheet U, et al. Attempted and completed
suicide in older subjects: results from the WHO/EURO Multicentre Study of
Suicidal Behaviour (2001) Int J Geriatr Psyi 16: 300-310. https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.337 53. Olsson G I
and Knorring A L. Adolescent depression: prevalence in Swedish high-school
students (2007) Acta Psyi Scand 99: 324-331.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.1999.tb07237.x
54. ELKLIT A.
Victimization and PTSD in a Danish National Youth Probability Sample (2002) J
Am Academy Child Adol Psyi 41: 174-181. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-200202000-00011
55. Blum R W,
Halcón L, Beuhring T, Pate E, Campell-Forrester, et al. Adolescent Health in
the Caribbean: Risk and Protective Factors (2003) Am J Public Healt 93:
456-460. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.93.3.456
56. Rabe-Jablonska
J, Gmitrowicz A, Szymczak W and Kropiwnicki P. Gender influence in suicidal
behaviour of Polish adolescents (2003) Europ Child Adol Psyi 12: 205-213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-003-0331-5
57. Toros F,
Bilgin N G, Sasmaz T, Bugdayci R and Camdeviren H. Suicide Attempts and Risk
Factors Among Children and Adolescents (2004)
Yonsei Med J 45: 367. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2004.45.3.367
58. Zemaitiene
N and Zaborskis A. Suicidal tendencies and attitude towards freedom to choose
suicide among Lithuanian schoolchildren: results from three cross-sectional
studies in 1994, 1998, and 2002 (2005) BMC Public Healt 5: 83. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-5-83
59. Young R,
Sweeting H and West P. Prevalence of deliberate self-harm and attempted suicide
within contemporary Goth youth subculture: longitudinal cohort study (2006) BMJ
332: 1058-1061. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38790.495544.7c
60. Sidhartha
T and Jena S. Suicidal behaviors in adolescents (2006) Indian J Pediatrics 73:
783-788. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02790385
61. Dervic K,
Akkaya-Kalayci T, Kapusta ND, Kaya M and
Merl E. Suicidal ideation among Viennese high school students (2007)
Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 119: 174-1780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-006-0753-4
62. Silviken A
and Kvernmo S. Suicide attempts among indigenous Sami adolescents and majority
peers in Arctic Norway: Prevalence and associated risk factors (2007) J
Adolescence 30: 613-626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2006.06.004
63. Gex CR,
Narring F, Ferron C and Michaud PA. Suicide attempts among adolescents in
Switzerland: prevalence, associated factors and comorbidity (1998) Acta Psyi
Scand 98: 28-33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.1998.tb10038.x
64. Tousignant M, Habimana E, Biron C, Malo C,
Sidoli-lebianc E, et al. The Quebec Adolescent Refugee Project: Psychopathology
and Family Variables in a Sample From 35 Nations (1999) J Am Academy of Child
Adol Psyi 38: 1426-1432. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199911000-00018 65. Miauton L,
Narring F and Michaud PA. Chronic illness, life style and emotional health in
adolescence: results of a cross-sectional survey on the health of
15-20-year-olds in Switzerland (2003) European J Pediatrics 162: 682-689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-003-1179-x
66. Yip PSF,
Liu KY, Lam TH, Stewart SM, Chen E, et al. Suicidality among High School
Students in Hong Kong, SAR (2004) Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior 34:
284-297. https://doi.org/10.1521/suli.34.3.284.42772
67. Rodríguez
AH, Caldera T, Kullgren G and Renberg ES. Suicidal expressions among young
people in Nicaragua (2006) Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 41:
692-697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-006-0083-x
68. Rudatsikira
E, Muula AS and Siziya S. Prevalence and associated factors of suicidal
ideation among school-going adolescents in Guyana: results from a cross
sectional study (2007) Clini Pract Epidemiol Mental Healt 3: 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-0179-3-13
69. Kaltiala-Heino
R, Rimpela M, Marttunen M, Rimpela A and Rantanen P. Bullying, depression, and suicidal
ideation in Finnish adolescents: school survey (1999) BMJ 319: 348-351. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.319.7206.348
70. Khokher S
and Khan MM. Suicidal Ideation in Pakistani College Students (2005) Crisis 26:
125-127. https://doi.org/10.1027/0227-5910.26.3.125
71. Liu X,
Tein JY, Zhao Z and Sandler IN. Suicidality and correlates among rural
adolescents of China (2005) J Adolesc Healt 37: 443-451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2004.08.027
72. Weissman
MM, Bland RC, Canino GJ, Greenwald S, Hwu HG, et al. Prevalence of suicide
ideation and suicide attempts in nine countries (1999) Psychol Med 29: 9-17. 73. Nock MK,
Borges G, Bromet EJ, Alonso J, Angermeyer M, et al. Cross-national prevalence
and risk factors for suicidal ideation, plans, and attempts in the WHO World
Mental Health Surveys (2008) Br J Psychiatry 192: 98-105. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.107.040113 Gautam Anand, Department of psychiatry, Muzaffarnagar medical
college, Muzaffarnagar, Uttar Pradesh, India, Tel: 919406821491, E-mail:
drganandgwl@gmail.com Anand G. Typifying and characterizing suicide
and its dynamics of progression towards completion: A model (2019) Edelweiss
Psyi Open Access 3: 14-19. Suicide, Celebrate self-harm, Attempt and Completion.Typifying and Characterizing Suicide and its Dynamics of Progression towards Completion: A Model
Gautam Anand
Abstract
Conclusion: Everyone in their life
at least has to wish to die but very few complete it. It progress in certain
path as wish further strengthen by idea following celebrate self-harm may
repeat or accidentally completed if not further proceeded to take attempt. It
may be completed or rest as further are risk of suicide. Full-Text
Introduction
Review of
literature

Aim and
Objective
Selected more than 50 papers and documents available on different site
study evaluated and analyzed logically and best suited data available across
word wide on internet were sequential arranged. They were put in series may
appear in the form of trends to reach completion were considered. Discussion
and Interpretation
Conclusion
References
*Corresponding
author
Citation
Keywords