Commentary :
Tomohiro Yokoyama and Hiroshi Bando Background: In the field of psychology and psychosomatic
medicine, Transactional Analysis (TA) was and developed by Berne and Dusey.
Consecutively, egogram analysis has been prevalent by 5 egos including Critical
Parent (CP), Nurturing Parent (NP), Adult (A), Free Child (FC) and Adapted
Child (AC). In Japan, Tokyo University Egogram (TEG) has been used, and authors
have continued egogram research for long. Methods and Results: Subjects were 502 university students. They answered
TEG questionnaire with the evaluation of the personality trait. Out of 29
personality pattern, 6 types were more than standard data. They are dependent,
short-tempered, self-centered, conflict, solitude and pessimist types. During
10 years of our research, self-centered and solitude have been increasing, and
good-hearted and playboy types have been decreasing. Discussion: From
current data, several tendency would be speculated: Lower NP seems to be a
characteristic for modern university students. It may be related with a
noticeable decline in overall morality among younger generations in Japan.
Furthermore, the prevalence of internet in the world may influence of the
behavior of young people. Not actual experience but information on the internet
can make them refrain from active human relations to others. These results
would be expected to become useful reference data. In recent years,
behavioral science and psychosomatic
medicine have become more crucial for many people living in stressful daily
lives. There have been several drastic changes in the world influencing our
usual health. From these situation, various practice and research concerning TA
has been applied [1]. TA is one of the self-analysis with easy and useful
method. After that, the development of TA has brought practical research for
egogram with five factors, which are Critical Parent, Nurturing Parent, Adult,
Free Child and Adapted Child [2]. From the psychological and psychiatric point
of view, egogram research has been related with personality, communication
skill, healthy life and feeling happiness in daily life [3]. Successively,
practical research of egogram was developed using Tokyo University Egogram in Japan. It
was revised for the adequate situation with the personality trend of Japanese
person for long years [4]. TEG has been known as reliable psychological test
with the standard data from statistical detail investigation [5]. As for the
egogram, authors have continued psychosomatic research of egogram for various
subjects. They include music therapist, music learner, adults and so on [6].
Furthermore, we developed egogram research for university students [7,8].
During our research, we reported various egogram changes for young generation
[9]. In particular, recent changes seem to be related to the internet
development in the world [10]. Consequently, authors have continued egogram
research for university students. We have investigated and compared our detail
data for years. These impressive data and discussion would be described in this
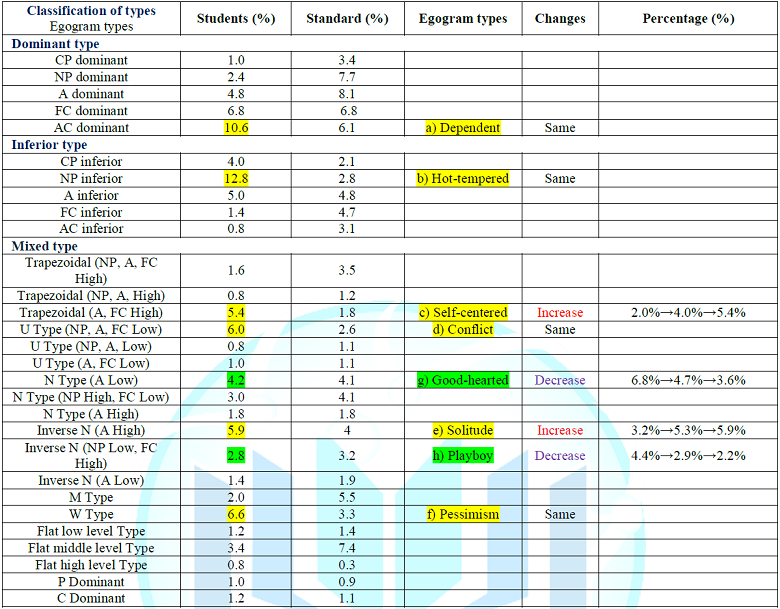
article. The results of
current study of the egogram are shown in Table
1. The subjects included 502 university students. The number and percentage
of three groups (dominant, inferior and mixed type) in Table 1 was 128 (25.6%),
120 (24.0%) and 254 (50.8%), respectively. We have been investigating the
situation of the egograms for university students until now. From these
results, six characteristic types from 29 types of TEG patterns were selected
which were more frequent than standard prevalence. They are i) dependent, ii)
short-tempered, iii) self-centered, iv) conflict, v) solitude, vi) pessimist. According
to our previous data, the changing patterns of these 6 types were investigated.
There were three periods, which were 2010-2013, 2013-2016, 2016-2019. The
tendency of frequency in 6 types was as follows. 1) There are four types of
almost same frequency during 10 years out of 6 high-frequency types. They are
i) dependent, ii) short-tempered, iv) conflict and vi) pessimist. 2) Increasing
frequency types were found during 10 years. They are iii) self-centered type
(2.0%→4.0%→5.4%), and v) solitude type (3.2%→5.3%→5.9%). 3) In contrast,
decreasing frequency types were found. They are good-hearted type
(6.8%→4.7%→3.6%) and playboy type (4.4%→2.9%→2.2%). Table 1: Results of
the egogram types. The egogram test has
been useful and significant in the light of psychological aspects. It is
related with self-consciousness,
behavior, attitude and mutual communication [11]. It can be also helpful
medically and socially for better life [12]. There is several meaningful
research of egogram for several diseases or various states. They include
pregnancy, hypertension, and patients with personal traits, subjects related
with organ
transplantation, scientific researchers, and others [13-16]. Consequently,
egogram has been used for various purposes in medicine, education and economic
fields. In this study, a characteristic tendency was consistently observed that
the NP factor showed low value levels among the five factors of the egogram. Out of 6 types with
high frequency (a-f), 5 types showed low NP (b-f) were found. This seems to be
a characteristic data of modern university students [9]. There has been
recently a noticeable decline in overall morality among younger generations in
Japan. Among them, some students have not accepted the results of i) very low
level of NP factor in the results of the questionnaire, and ii) testing method
and interpretation of TEG [10]. Further, there are some students who do not try
to realize the low NP or change their current egogram. An impressive datum has
been found in the point that there is no willingness to change the current
situation. The related question would be whether the person has the ideal image
or not. In every year, there are about 20% of university students who answer no
need at all to change him for the ideal situation. Those students are
involved in several egogram types, including short-tempered, pessimist, free
spirit, dependent and playboy (92-Yoko) [7]. For these circumstances, we cannot
decide whether they are the problems of frequency, types, individual character
or each way of thinking. Among the 5 factors in the egogram, the NP factor
arises from the relationship between mother and child. Therefore, NP seems to
present the basis of the mutual connection and communication between people
[2]. In the past, NP factor was rather higher than other factors in each
generation in Japan [4]. For middle to aged people, NP dominant (kind mother or
nursemaid type) has
been observed most frequent in Japan as 15.8% [17]. As there have been a
variety of changes for westernized and individualism society, the value of NP
factor has been decreasing. Further, the prevalence of internet world has also
influence the tendency. Furthermore, the NP factor seems to have gradually
decreased over the decade of our survey research. In addition to the above,
episodes that lower NP are observed in our daily life. There are some examples:
1) when a young person tries to give a seat to an elderly person in the bus or
train, the elderly refuses to accept the proposal, 2) when an unconscious women
is found and immediately managed for Automated External
Defibrillator (AED), such behavior may be regarded as sexual harassment.
Those behaviors have been essentially kind actions. However, the episodes that
happened to intervene in others with good intentions may be misunderstood and
judged to be malicious. Those episodes seem to be rare, but such cases are
widely known through the Internet [9]. As a result, the younger generation who
come in contact with this information will refrain from intervening in others
with kindness. In the modern
Internet system, everyone has the ability to share comments on the articles
written by others [18]. Therefore, we can easily know various opinions of
others. However, there are many people who agree with certain articles that
misunderstand the original behavior of kindness. Younger generations with
little experience may have high AC
and low A factors. Then, such rare
opinions that are observed on the Internet may be evaluated as the majority of
opinions from many people [19]. As a general rule,
there is a bias in humans who often enter comments on the Internet [18]. There
are many types of people who want to assert themselves. Further, the opinions
of those who are aggressive
and strongly asserted are widely reflected, and their contents are wrong or
biased. Therefore, there is a possibility of receiving wrong information. As
the factor A shows low level, only
the rare information in front of the eyes may be believed, and statistically
the majority of standard trend and evaluation are misread. Young readers
themselves may decrease NP by agreeing to such biased opinion. From current data, it
was the same as before that there were still many cases of short-tempered
types. We will focus on the increase tendency in the types of free spirit and
solitude. Regarding the increase of the free spirit type, this seems to be
attributed to the fact that students can enter the universities successfully in
Japan [20]. The reason would be that students have been greatly repressed by
studying for exams up to high school. It lasted for long years for them, and
escaping such stressful days made them happy. The daily life at university is
completely different from the previous one, with free life as they like. Some
examples include living away from their parents, experiencing part-time work,
playing with friends until late at night, and so on [21]. Furthermore, how do
modern students observe four years in the university? They seem to evaluate it
living with a high degree of freedom, rather than acquiring fundamental
knowledge of education and culture necessary for future life as a member of
society. In this way, it can be speculated that the FC factor of students will
be increased and exploded from the educational situation and then FC dominant
type will be common after entering the university [20,21]. On the other hand,
the solitude type has been belonged to the category of self-centered type,
and is a type that sticks to self-assertion [22]. Since the feature is a high
factor CP, there is a tendency to strongly criticize others. For this reason,
in the Internet exchange sites that have been spreading in recent years, the
assertion of biased opinions may continue for long and cause the so-called flame
up. According to many
reports on egograms, there is a specific background for the person of solitude
type. That is the presence of accumulated dissatisfaction because they have
been unable to pass on their self-assertion [22].
From the viewpoint of a suppressed life, there is a common point between the
above-mentioned free spirit type and the solitude type currently discussed. In
the former, however, the CP is low and the NP is maintained, so that the
aggressive behavior has been rare. In the latter, the high CP and the low NP
has been important points to cause various inadequate behaviors [10]. By both
factors, the direction of releasing the depressed emotion may proceed to the
criticism without consideration for others. Concerning the both
types which are free spirit and the solitude types, there is another comparison
from different perspectives. It is indeed that both have depressed lives and
common reaction to various changes that are more restrictive in the society.
However, the different matter is the perception and recognition for the
regulations present in the society. In other words, it is considered that some
types are derived from the difference, whether regulation or rule is i)
important, ii) possible, iii) accepted as possible, iv) impossible and so on
[23]. FC factors are generally found at high levels in the subject of
university students. For this reason, two groups would be probably present in
the students. Group1 includes students who showed increased FC factor by releasing
from the suppressed state in the high school. Group 2 includes students who
showed stable FC factor level as before. This is difficult to compare because
there are no data of egograms a few years ago when they were high school
students [24]. In our study, however, there was a case that showed rapid
increase of FC factor, after several months of entering the university. From
the above, it is suggested that the value of FC may change significantly in a
relatively short period of time by enrolling in a free student life [25]. The
authors speculate that FC change would be larger when compared to just a few
months after entering university [11]. A comparative study
can be possible in two groups, one with FC changes and one with no change.
Several reasons may be involved in the difference, such as whether the subject
can be accustomed to the school life and friends, whether he lives with his
parent or only himself, whether some differences are present in club activities
or curriculum [24,25]. If the situation permits, more detailed investigations
can be possible. Then, interesting results may be obtained if there are basic
researches, follow-up research, counseling and so on. In summary, study of
egogram type for students showed that 6 types were more than standard data.
They are dependent, short-tempered,
self-centered, conflict, solitude and pessimist types. During 10 years of our
research, self-centered and solitude have been increasing, and good-hearted and
playboy types have been decreasing. Current results would be expected to become
a fundamental reference for further development of research. 1.
Berne
E. Ego states in psychotherapy (1957) Am J Psychother 11: 293-309. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.psychotherapy.1957.11.2.293 2.
Dusay
J. Egograms-How I see you and you see me (1977) Harper and Row, USA. 3.
Steiner
CM. Scripts People Live: Transactional Analysis of Life Scripts (1990) Grove
Press, USA. 4.
Kuboki
T, Nomura S, Wada M, Akabayashi A, Nagataki M, et al. Multidimensional
assessment of mental state in occupational health care-combined application of
three questionnaires: Tokyo University Egogram, Time Structuring Scale and
Profile of Mood States (1993) Environ Res 61: 285-298. https://doi.org/10.1006/enrs.1993.1073 5.
Psychosomatic
medicine department of Tokyo University (1995) Egogram pattern new edition,
Personality analysis, Kaneko publishing, Japan. 6.
Yoshioka
A, Bando H and Yoshioka T. Effect of musical experience on optimization of
egogram (2004) Jap J Music Ther 4: 191-197. 7.
Yokoyama
T and Bando H. Study of Personality Traits for University Students by Egogram
Analysis (2018) Biomed J Sci Tech Res 9. http://dx.doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2018.09.001797 8.
Bando
H and Yokoyama T. Use of Egogram for Psychological Development of the
Adolescence (2018) Psychol Behav Sci Int 002 J 9: 7116-7119. http://dx.doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2018.09.001797 9.
Yokoyama
T and Bando H. The Egogram Feature of Late Teenager in the Internet Generation
(2018) Clin Res Psychol 1: 1-4. 10.
Bando
H and Yokoyama T. Various Strokes for Development of Ego in the Transactional
Analysis (2018) Mathew J Psychol 3: 20. 11.
Yoshiwara
K and Tsuchiya H. Correlations among focusing attitudes, psychological
competitive abilities and public self-consciousness in college athletes (2019)
Person-Centered Exp Psychotherap 18: 85-97. https://doi.org/10.1080/14779757.2019.1572028 12.
Bando
H. Psychological Study of Egogram can be Helpful medically and socially for
Better Life (2018) Archives Psyi Behav Sci 1: 11-14. 13.
Kobashi
G, Ohta K, Shido K, Hata A, Yamada H, et al. The egogram is a potent,
independent risk factor for hypertension in pregnancy (2005) Semin Thromb
Hemost 31: 302-306. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-872436 14.
Sugiyama
T, Yamakura D, Tomita S, Kameyama A, Morinaga K, et al. Personality traits in
patients with oral malodor (2014) Bull Tokyo Dent Coll 55: 233-239. https://doi.org/10.2209/tdcpublication.55.233 15.
Nishikawa
K, Hasegawa T, Usami A, Urawa A, Watanabe S, et al. Pre-operative Assessment of
Psychological Characteristics and Mood States in Living Donor Kidney and Liver
Transplantation (2016) Transplant Proc 48: 1018-1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.12.122 16.
Sakagami
Y. Qualitative job stress and ego aptitude in male scientific researchers
(2016) Work 55: 585-592. https://doi.org/10.3233/wor-162427 17.
Shinoda
T, Nakashita S, Hamada M, Hirono K, Ito M, et al. Egogram characteristics in
Japanese patients with Parkinsons disease (2018) Neurol Clin Neurosci 6: 71-76.
https://doi.org/10.1111/ncn3.12189 18.
Chung
TWH, Sum SMY and Chan MWL. Adolescent Internet Addiction in Hong Kong:
Prevalence, Psychosocial Correlates and Prevention (2019) J Adolescent Healt
64: 34-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.12.016 19.
Vriens
E and Van Ingen E. Does the rise of the Internet bring erosion of strong ties?
Analyses of social media use and changes in core discussion networks (2018) New
Media Society 20: 2432-2449. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444817724169 20.
Kuramoto
N and Koizumi R. Current issues in large-scale educational assessment in Japan:
focus on national assessment of academic ability and university entrance
examinations (2016) Assessment Education: Principles, Policy Prac 25: 415-433. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969594x.2016.1225667 21.
Komatsu
H and Rappleye J. Is exam hell the cause of high academic achievement in East
Asia? The case of Japan and the case for transcending stereotypes (2018) Br Edu
Res J 44: 802-806. https://doi.org/10.1002/berj.3468 22.
Park
B, Ibayashi K and Matsushita M. Classifying Personalities of Comic Characters
Based on Egograms (2018) Int Symp Affect Sci Engineering 1-6. https://doi.org/10.5057/isase.2018-c000029 23.
Schütte
N, Blickle G, Frieder RE, Wihler A, Schnitzler F, et al. The Role of
Interpersonal Influence in Counterbalancing Psychopathic Personality Trait
Facets at Work (2016) J Management 44: 1338-1368. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206315607967 24. Saitou T,
Sugahara T and Kato C. A Study on the Self-Affirmation of University
Student-Focusing on Classification by Personality (2018) 7th
International Congress on Advanced Applied Informatics, Japan, https://doi.org/10.1109/iiai-aai.2018.00110 25. Eun-Hyeon J and Dong-Hyung L. The effect of
personality traits on stress and academic achievement (2018) Ind J Pub Health
Res Dev 9: 1374-1379. https://doi.org/10.5958/0976-5506.2018.01183.x Hiroshi Bando, Medical
Research, Tokushima University, Nakashowa 1-61, Tokushima 770-0943, Japan, Tel:
+81-90-3187-2485, E-mail: pianomed@bronze.ocn.ne.jp Yokoyama T and Bando
H. Characteristic egogram state of younger generation (2019) Edelweiss Psyi
Open Access 3: 25-28. Egogram, Tokyo university egogram, Transactional
analysis, Personality trait, Psychological development.Characteristic Egogram State of Younger Generation
Abstract
Full-Text
Introduction
Results
Discussion
References
Corresponding author:
Citation:
Keywords